1 5V to 5V 12V DC DC Converter with LT1073
Friday, September 26, 2014 | Labels: 1, 12v, 5v, converter, dc, lt1073, to, with | 0 comments |













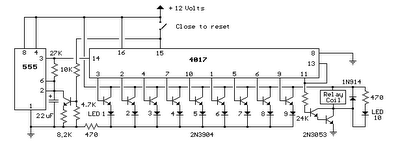
This is door knob touch alarm for your home security purpose. The alarm will be activated when someone touch the metal door knod. This circuit won’t work on full metal door.
Download the schematic drawing
The following circuit is a simple, cheap and easy build motorcycle alarm. The circuit just required 2 transistors to drive the relay the the relay act as a switch to activate the buzzer.
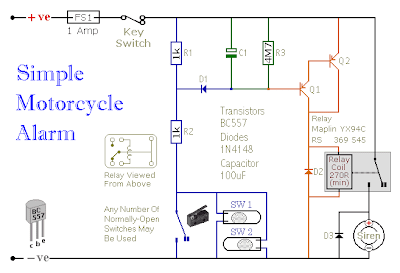
Any number of normally-open switches may possibly be applied. Fit the mercury switches to ensure that they close when the steering is moved or when the bike is lifted off its side-stand or pushed forward off its centre-stand. Use micro-switches to secure removable panels as well as the lids of panniers and so on. Although at the very leastonce again – the alarm will reset. How lengthy it takes to switch off depends upon the characteristics of the actual parts you have utilized. You are able to adjust the time to suit your requirements by changing the value of C1 and/or R3.

The circuit board and switches need to be protected from the elements. Dampness or condensation will trigger malfunction. With out its terminal blocks – the board is small. Ideally, you need to attempt to locate a siren with sufficient spare space inside to accommodate it. Fit a 1-amp in-line fuse as close as achievable to the power source. This is Extremely Crucial. The fuse is there to secure the wiring – not the circuit board. Rather than utilizing a key-switch you’ll be able to use a hidden switch; or you could use the normally-closed contacts of a tiny relay. Wire the relay coil to ensure that it is energized whilst the ignition is on. Then each and every time you turn the ignition off – the alarm will set itself.
When it is not sounding – the circuit uses practically no present. This need to make it helpful in other circumstances. For instance, powered by dry batteries and using the relay and siren voltages to suit, it might be fitted inside a personal computer or anything else that is in danger of becoming picked up and carried away. The low standby electric current and automatic reset indicates that for this sort of application an external on/off switch might not be essential.
Easy build motorcycle alarm circuit source: www.zen22142.zen.co.uk