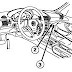
Basically the DAC circuit is made to meet the need for the level of influence in the development of digital electronic circuits electronics world.
Since the discovery of Silicon and Germanium semiconductor material then quickly there was a revolution in terms of simplicity and accuracy of an electronic circuit. Besides, with the implementation of digital circuits will support at all in terms of data storage and mobility. Lots of data can now be operated with a computer is a data converted from analog signals. For example a voice signal or analog form of video can be played and stored using a computer after analog signals are converted into digital data.

Advantages possessed by the digital data than analog signal is a certainty the nature of the data or logic. Digital data only can be divided into two kinds of logic high "1" and logic low "0". Logic 1 represents 5 volts and low logic voltage 0 volts represents. Examples of the advantages of digital signals over analog signals is on television or digital radio receiver. By implementing a digital system signals emitted by television or radio stations will form the data 1 and 0, so at the time of the transmission or delivery of data signals that change or damaged by the interruption of transmission will hardly change the logic of the signals. But if the transmitted signal is the original signal in the form of an analog signal then if just a little damage due to interruption of transmission, the signal to be received is a signal that has been damaged serve targeted.
In the DAC circuit above uses two LM741 Op-Amp IC is often used as an amplifier. IC1 to function as a producer of analog signal is reversed, and turned back IC2 function signal from IC1. Basic circuit of the DAC is a common amplifier circuit, only used a variation of several resistors in order to obtain a regular reinforcement signal. Rules that must be understood from this DAC circuit is the value of resistors on the input op-amp. The value for the resistor at high bit (R4) should be 2x the amplifier resistor (R5), then for the next bit should be 2x the resistor value at a higher bit. So if the circuit uses 4-bit DAC is the unit bit (lowest bit) is the value of bits to be 8x-4. From the picture above the unit bit is represented by resistor 80 Kohm.
Sample Conditions:
- 0001 (1) = switch SW1 closed and others opened, the voltage output produced is (5K/80K) x 9 volt = 0.5625 volts
- 0010 (2) = SW2 is closed and another switch is opened, the output voltage is (5K/40K) x 9 volts = 1.125 volts
- 0011 (3) = SW1 and SW2 is closed and another switch is opened, the voltage output is (5K/Rparalel 80K and 40K) x 9 volt = (5K/26, 667K) X 9 volt = 1.6875 volts
- 1000 (8) = SW4 is closed and another switch is opened, the output voltage is (5K/10K) x 9 volts = 4.5 volts.
From the above calculation can be concluded that unlicensed with a voltage output proportional to the input conditions, eg for 1 decimal is 0.5625 volts then, decimal 2 = 2 x 0.5625 = 1125 volts, decimal 3 = 3 x 0.5625 = 1.6875 volts, and so on. This condition is due to the parallel relationship between the input resistors.